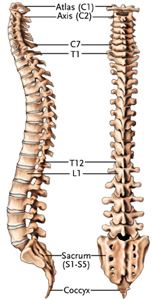
 The human spine consists of 33 vertebrae:
The human spine consists of 33 vertebrae:
The sacrum and coccyx are made up of 9 fused vertebrae
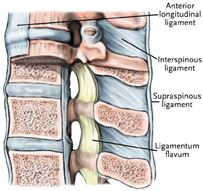
Each vertebra is attached to the one above and below it by ligaments and
muscles. They are separated from the vertebra above and below it by an
intervertebral disc. Two vertebra and the disc between them make up a
motion segment.
Facet joints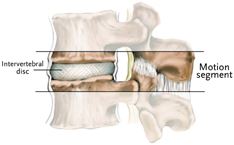
Formed by the overlapping of the projections from the lamina. The upper projection of one lamina (superior articular process) is overlapped by the lower projection (inferior articular process) of the adjacent vertebra and together form the facet joint.
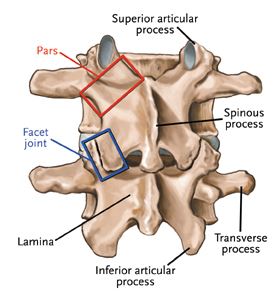
There is a facet joint on each side of the spine at every level.
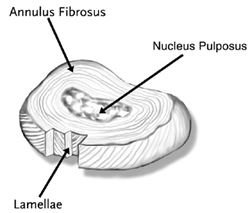
Intervertebral Disc
The structure that separates two vertebrae
Consists of:
A normal disc is so strong that it can be damaged only by extreme forces. A normal, healthy disc is one of the best parts of the spine.
An opening between the pedicles of the vertebrae through which nerve roots exit off the spinal cord.
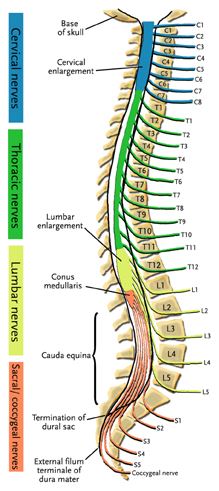
Spinal canal
Contains the spinal cord from the brain stem to the upper lumbar spine.
There is no spinal cord in the lower lumbar spine. At the L1 level, the spinal cord terminates as the conus medullaris.
Foramen
A bundle of nerves called the cauda equina (meaning horse's tail) branch off the conus medullaris. These nerve roots are suspended in the fluid-filled dural sac.